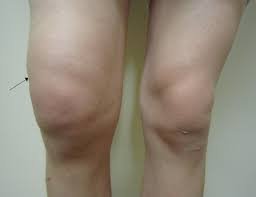
If you’re experiencing swelling in just one knee, there could be several possible causes. Here are some of the most common reasons and when to seek medical attention:
Possible Causes of One Swollen Knee:
-
Trauma or Injury
-
Sprains, strains, or ligament tears (e.g., ACL injury)
-
Fractures or meniscus tears
-
Bursitis (inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs around the knee)
-
-
Infections (Septic Arthritis)
-
Bacterial or viral infections can cause sudden, painful swelling, often with fever.
-
Requires immediate medical treatment to prevent joint damage.
-
-
Gout or Pseudogout
-
Gout (uric acid crystals) causes sudden, severe pain, redness, and swelling.
-
Pseudogout (calcium crystals) has similar symptoms but is less common.
-
-
Osteoarthritis (Wear-and-Tear Arthritis)
-
Typically affects one knee more than the other, especially in older adults.
-
May cause stiffness, pain, and swelling after activity.
-
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis (Autoimmune Condition)
-
Usually affects both knees, but early stages may start on one side.
-
-
Baker’s Cyst (Popliteal Cyst)
-
A fluid-filled sac behind the knee that can cause swelling and stiffness.
-
-
Blood Clot (Deep Vein Thrombosis – DVT)
-
If swelling is accompanied by warmth, redness, and calf pain, seek emergency care (risk of pulmonary embolism).
-
When to See a Doctor:
✔ Severe pain or inability to bear weight
✔ Fever, redness, or warmth (signs of infection)
✔ Sudden swelling after an injury
✔ Swelling lasting more than 3 days without improvement
At-Home Care (Mild Cases):
-
R.I.C.E. Method: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation
-
Over-the-counter pain relievers (NSAIDs like ibuprofen, if no contraindications)
If swelling persists or worsens, consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis (possibly X-rays, ultrasound, or fluid aspiration).
Would you like help identifying specific symptoms you’re experiencing?